Noise Abatement
How Boston Logan Operates
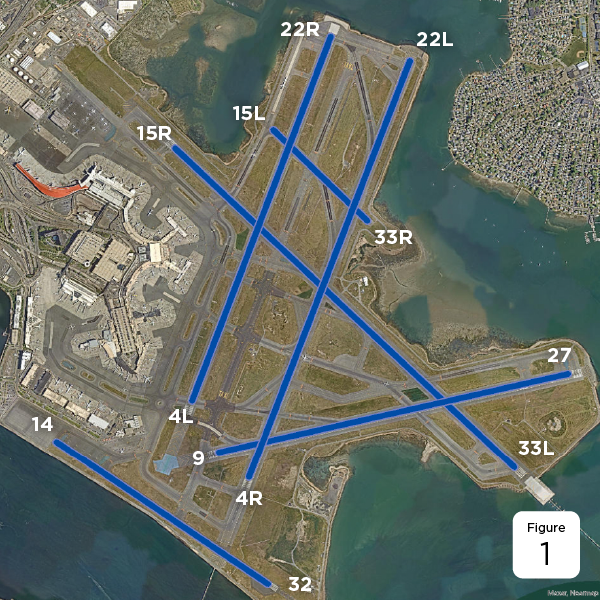
Boston Logan International Airport has six runways that vary in length from 2,557 feet to 10,081 feet. The runways are aligned in three directions, with each threshold pointing to a distinct magnetic heading. Generally, aircraft take off and land into the wind in ideal weather conditions. However, because Boston Logan is located on the coast, ideal wind conditions are far from common and are just one of the factors that are considered when the FAA selects a runway to use. Other factors include ground visibility, cloud coverage and ceiling, runway and taxiway availability, navigational aids available, aircraft fleet, and peak operational times.
During ideal weather conditions, Boston Logan can accommodate 120 operations per hour when the FAA can utilize a three-runway configuration. Runway capacity can be reduced to about 60 operations per hour in poor weather conditions and a single-runway configuration.
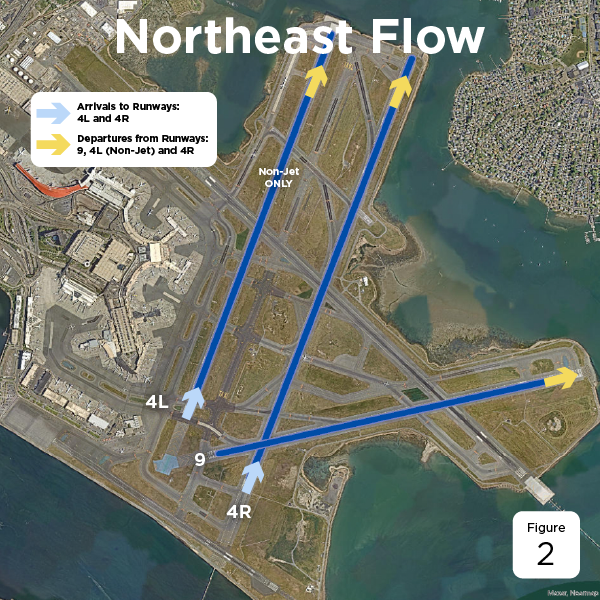
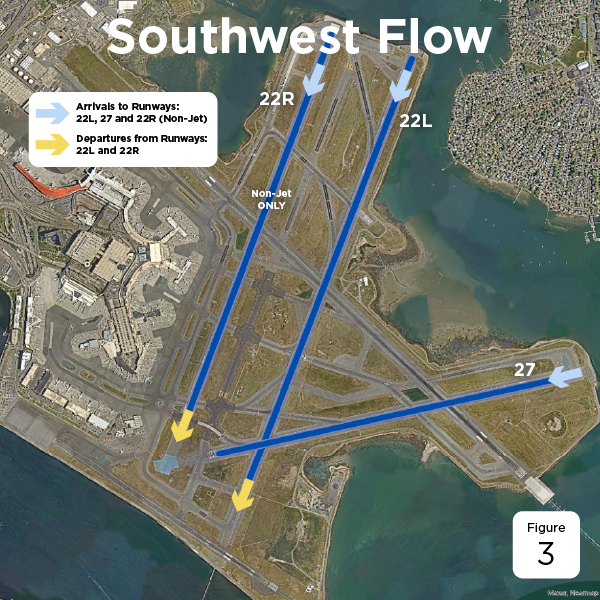
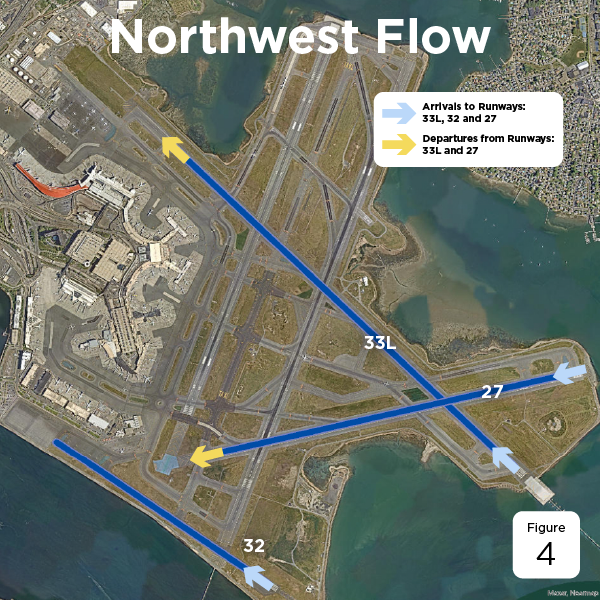
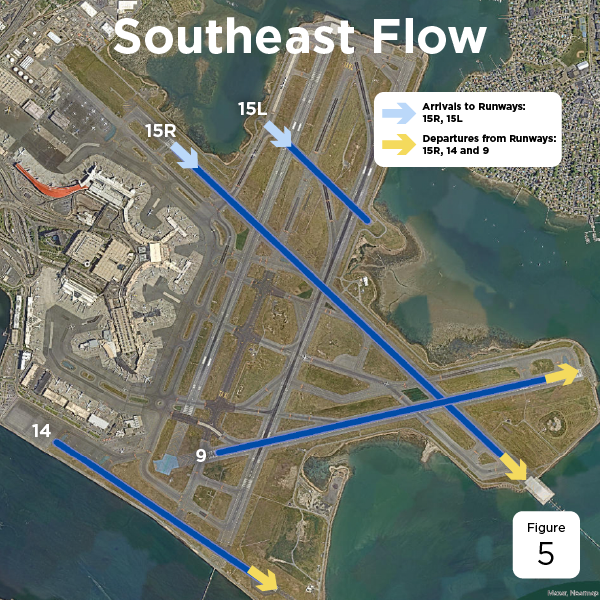
The weather trends at Boston Logan favor a northeast-southwest-northwest (NE-SW-NW) runway configuration. The chart below shows which runway configuration would be ideal in the specific conditions:
Primary Runway Configurations
| Wind Direction | Preferential Runway | Figure |
|---|---|---|
| North-East | 4L, 4R and 9 | 2 |
| South-West | 22L, 22R and 27 | 3 |
| North-West | 33L, 32 and 27 | 4 |
| South-East | 15L, 15R, 9 and 14 | 5 |